What is Transshipment Port and Hub Port?
Posted on: 30/10/2024
1. What is Transshipment Port?
A transshipment port is a port where goods, particularly containerized cargo, are unloaded from one vessel and loaded onto another. This usually occurs when direct routes aren’t available, or it’s more economical to transfer goods through a central point. Transshipment ports are often located along major shipping routes and serve as convenient interchange points for redirecting cargo.
Key Characteristics of Transshipment Ports:
-
Location: Positioned strategically on major trade routes, allowing for easy redirection of cargo to various parts of the world.
-
Container Capacity: Equipped to handle high volumes of container cargo, with facilities for both loading and unloading operations.
-
Efficiency in Transfer: Well-developed infrastructure for quickly moving cargo between vessels to minimize wait times and increase port efficiency.
Examples of Major Transshipment Ports:
-
Port of Singapore: Known as one of the busiest transshipment hubs globally, connecting Asia with Europe and the Americas.
-
Port of Tanjung Pelepas in Malaysia: A growing transshipment port benefiting from its location near Singapore, attracting major shipping lines.
-
Port of Algeciras in Spain: Serves as a critical transshipment point between Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
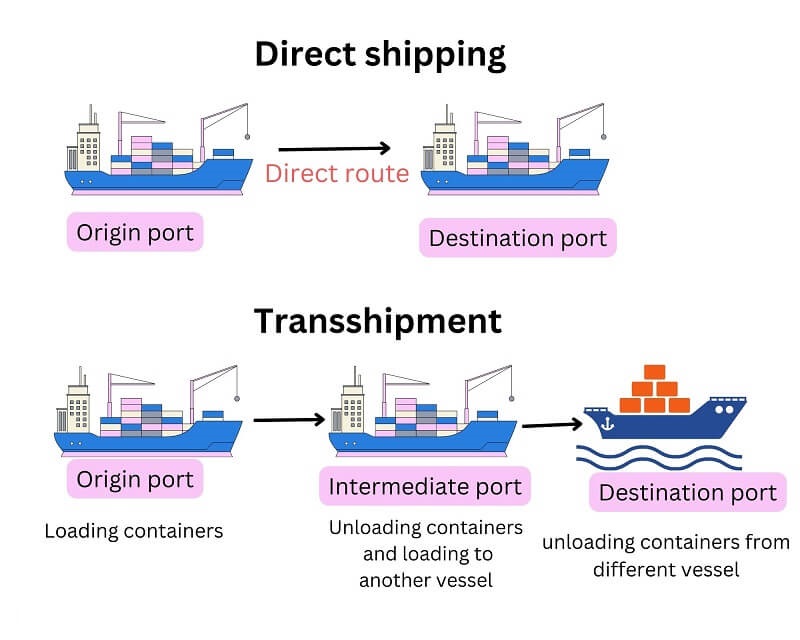
2. Hub Ports and Their Role in Trade
Hub ports are large ports that act as primary distribution points for shipping goods across various regions. They serve a central role in collecting and distributing cargo from multiple feeder ports (smaller regional ports). Hub ports are key assets in multimodal transportation networks, offering rail, road, and sea connections to efficiently handle and distribute goods.
Distinguishing Features of Hub Ports:
-
Regional Connectivity: Hub ports are well-connected to smaller, regional ports and other modes of transport, facilitating extensive cargo distribution.
-
Advanced Facilities: These ports have state-of-the-art infrastructure, including large storage facilities, cranes, and logistics centers to manage cargo flows seamlessly.
-
High Throughput: Equipped to handle massive volumes of cargo efficiently, supporting the rapid movement of goods across global supply chains.
Examples of Hub Ports:
-
Port of Rotterdam: Europe’s largest hub port, serving as the main gateway for cargo entering Europe from around the world.
-
Port of Dubai (Jebel Ali): A vital hub in the Middle East, connecting the East and West and supporting trade throughout the region.
-
Port of Los Angeles: A major U.S. port that serves as a hub for goods coming in from Asia, distributing across North America.
3. Why Transshipment and Hub Ports Are Important
Both transshipment and hub ports serve as essential links in the global logistics network, allowing for efficient cargo distribution. The interconnected nature of global trade means that these ports are not just transfer points; they’re economic engines that boost regional economies, support employment, and reduce overall shipping costs.
Benefits of Transshipment and Hub Ports:
-
Cost Reduction: By consolidating goods at one location, companies can save on direct shipping costs.
-
Improved Efficiency: Large ports are optimized for quick transfer and storage of goods, reducing transit times and improving supply chain efficiency.
-
Flexibility: These ports allow for easy rerouting of cargo, adapting to changes in demand or supply disruptions.
-
Economic Impact: Hub ports especially can attract investments, create jobs, and boost local economies.
4. The Future of Transshipment and Hub Ports
As global trade continues to expand, the demand for efficient transshipment and hub ports will only increase. To keep up, ports are investing in automation, digital technologies, and infrastructure expansion. This modernization aims to further enhance cargo handling, improve security, and reduce environmental impact through sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Transshipment and hub ports are integral to the logistics industry, facilitating smooth and cost-effective global trade. Understanding their role provides insight into the complex world of international shipping and highlights the importance of efficient logistics in today’s fast-paced economy. As you navigate the modern supply chain, keeping these essential ports in mind can help you better understand the strategies behind global trade success.
Whether you’re a business owner, logistics professional, or simply interested in global trade, transshipment and hub ports are worth knowing about as they continually shape the way goods move across the world.